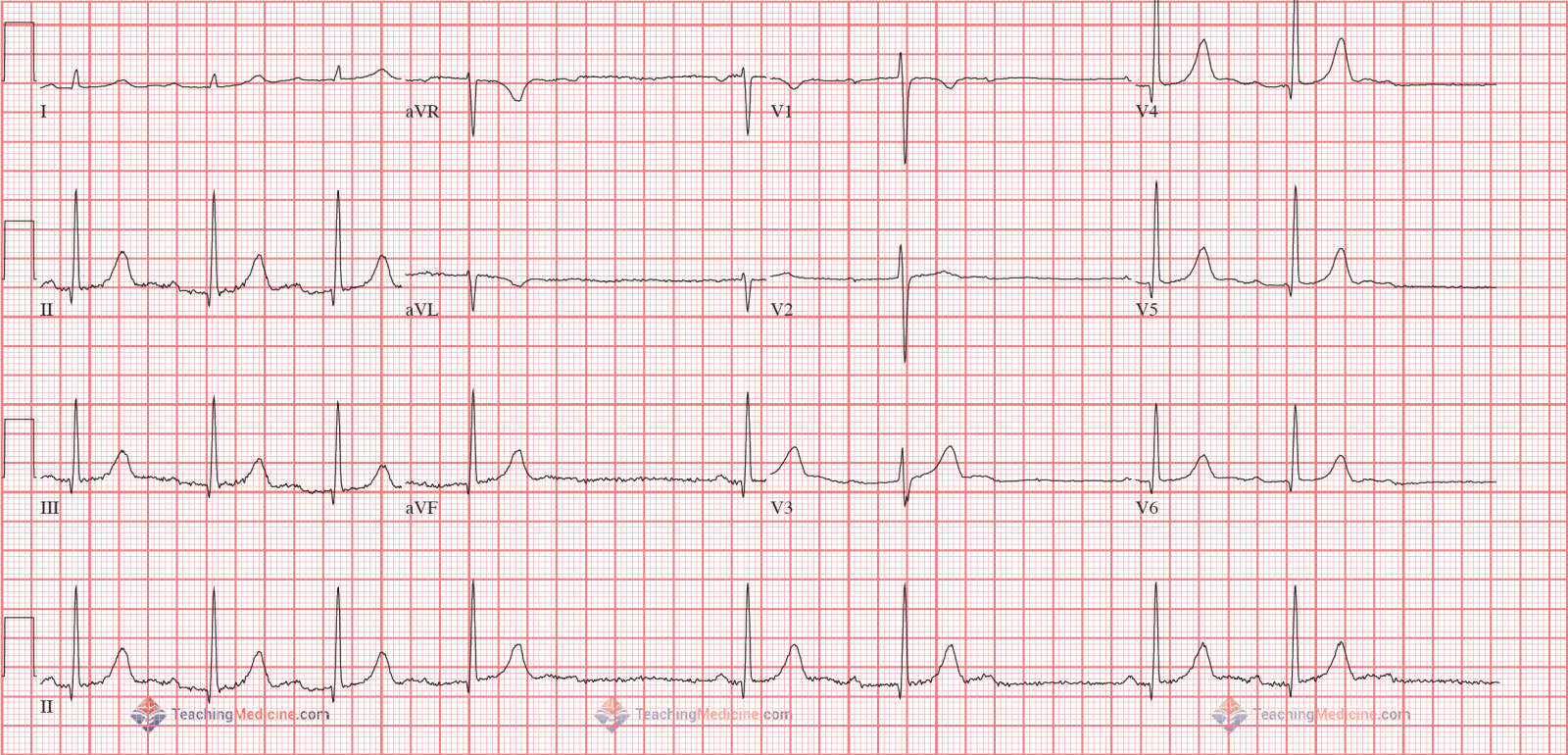
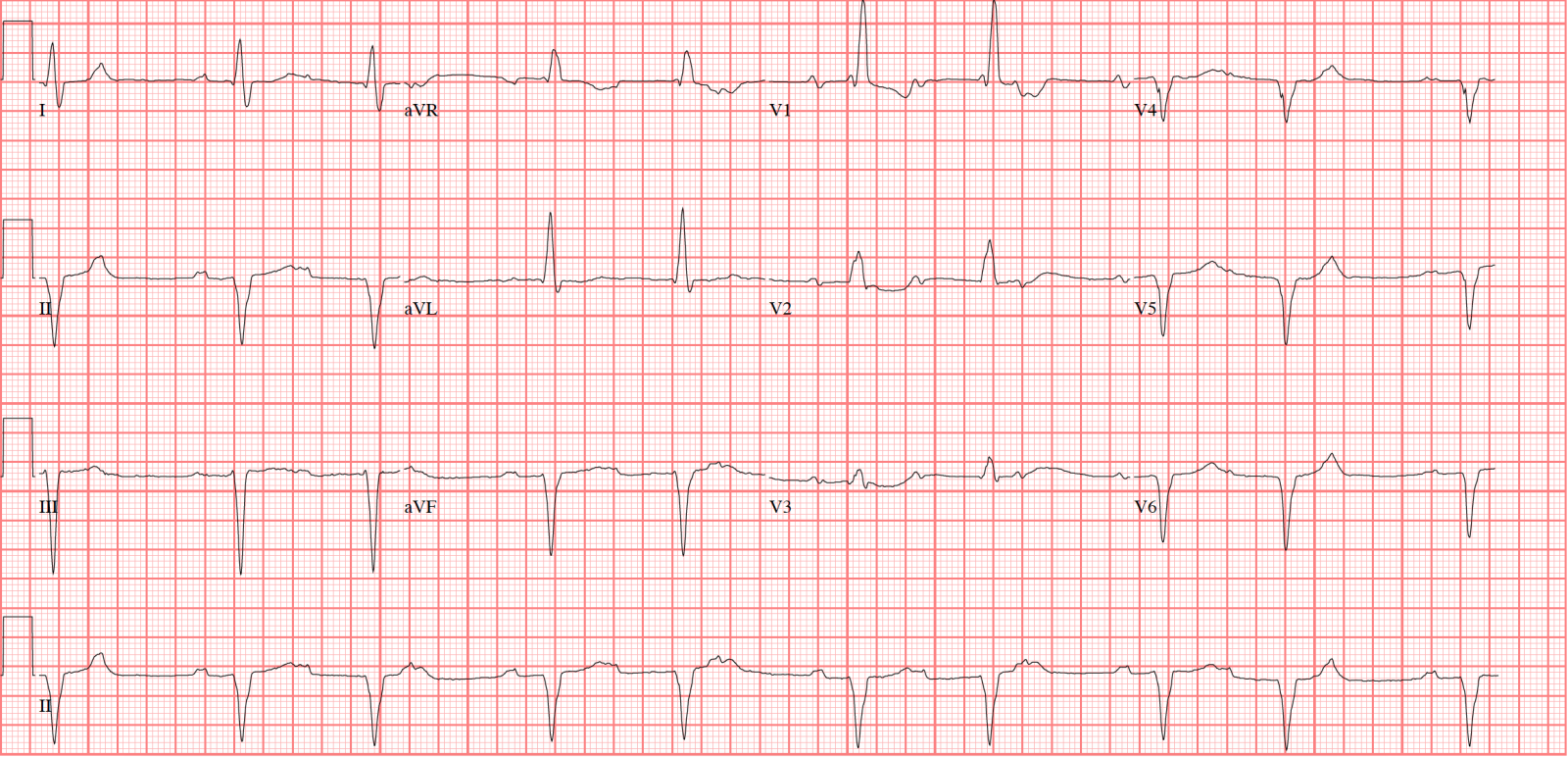
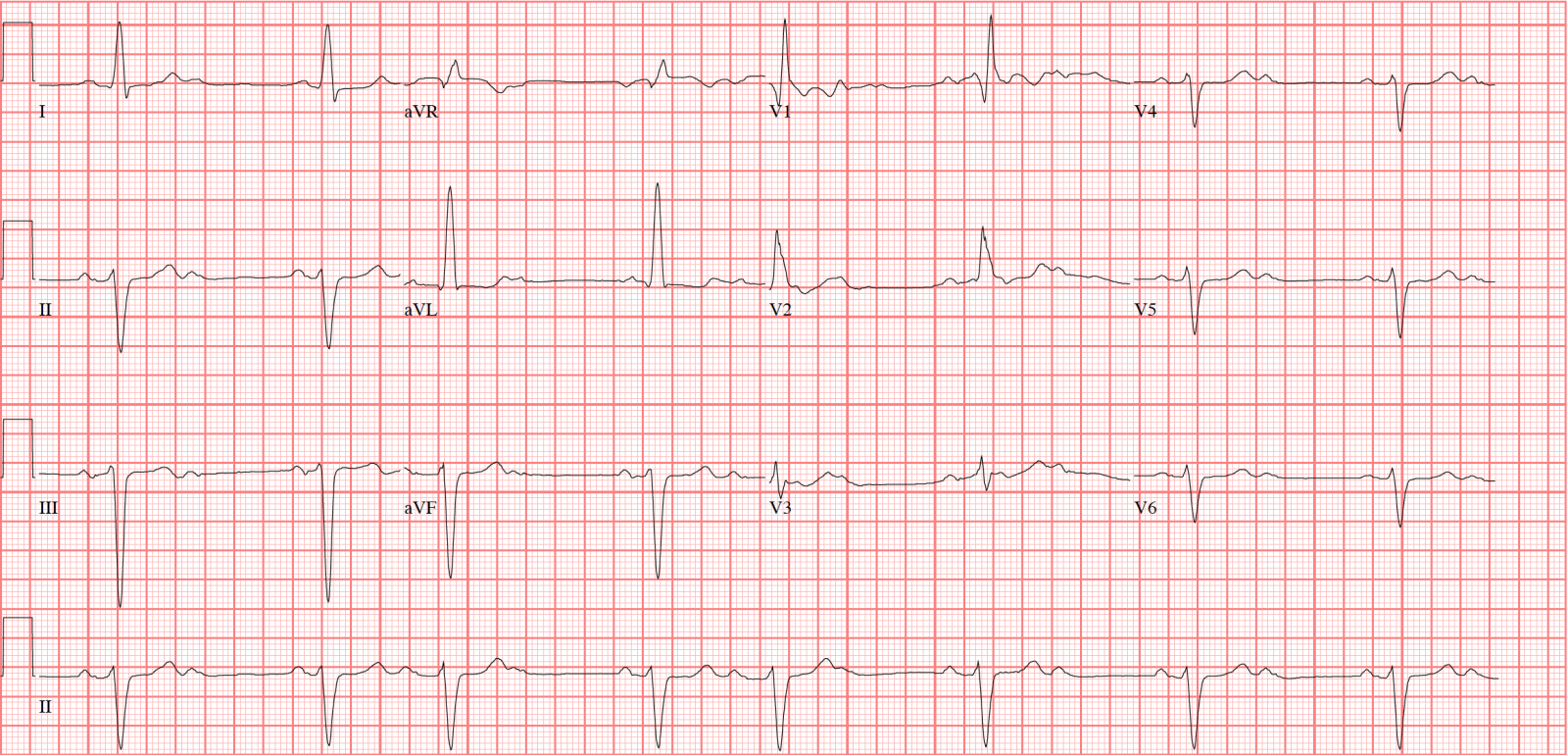
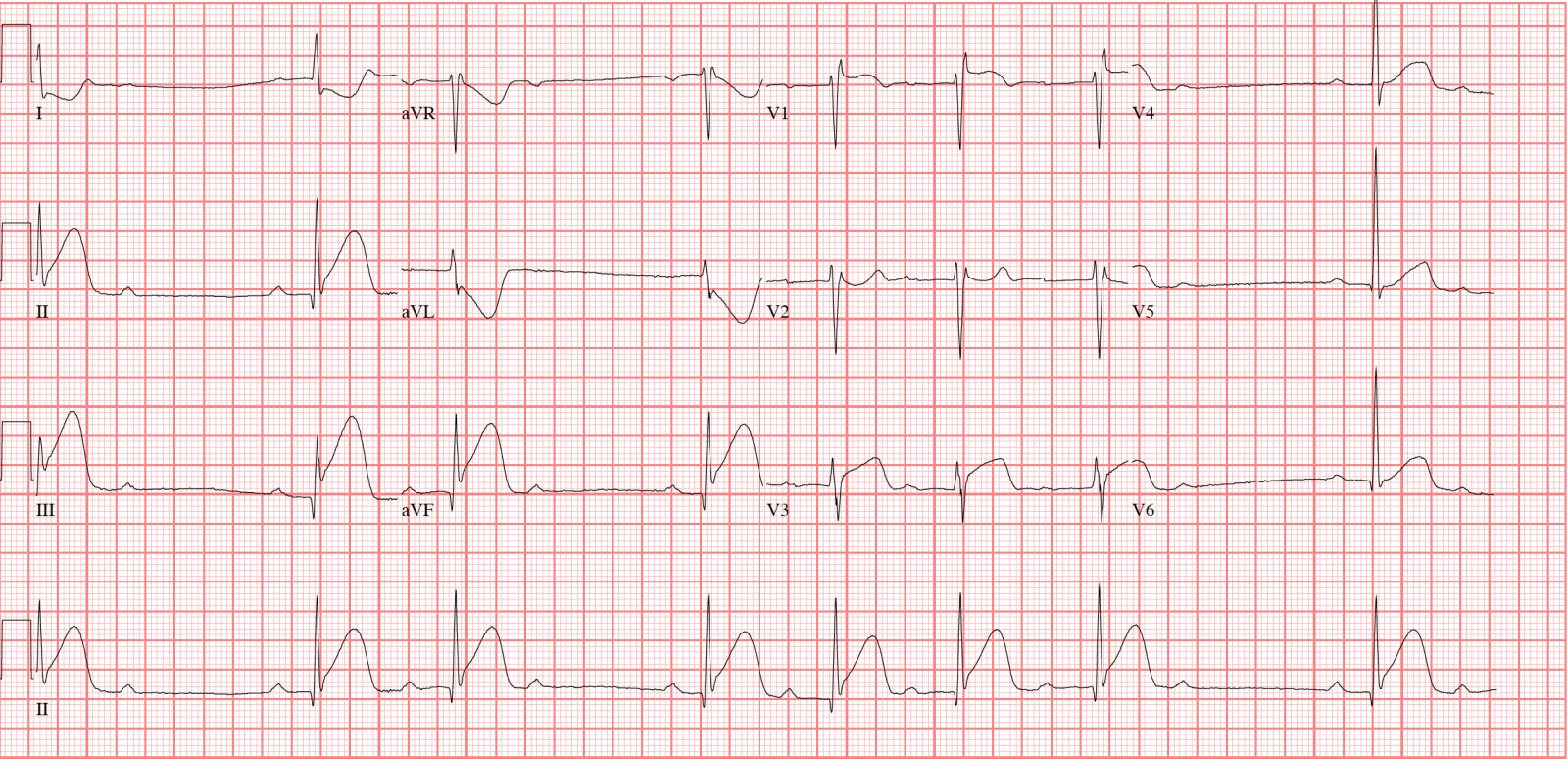
Second degree Heart Block Mobitz Type 1 (also called Wenckebach)
Diagnostic criteria: (boldfaced with * indicates an important feature)- Rate: any
- * Rhythm: regular with occasional missing beats
- P waves: all normal
- * PR interval: increasing with each heartbeat, resetting after missing QRS
- QRS: narrow
ElectrophysiologySome but not all the P waves are conducted in second degree heart block. In contrast, in first degree heart block, all the P waves are conducted
down to the ventricles and in third degree heart block, none of the P waves are conducted.
There are a few names for this heart block. They include:- second degree type 1
- Mobitz type 1
- Wenckebach
The difference between Type 1 and Type 2 second degree heart block:- Type 1 has increasing PR intervals, increasing until the QRS is "dropped" or missing
- Type 2 has constant PR intervals, with randomly dropped QRS complexes
It is complicated to explain exactly WHY the pattern of increasing PR intervals occurs and I won't try ... sorry :)
Typically, the location of the block is within the AV node. Less commonly, it can occur in the Bundle of His.
Clinical Significance:Some of the conduction from the atria to the ventricles is blocked. Therefore, the ventricular rate will be lower than the atrial rate. If the atrial rate is already borderline low, then the loss of a few conducted beats could result in a ventricular rate that is "too low" and causes problem. If this occurs, and the ventricular rate is low enough to cause symptoms, then a pacemaker might be required.
Second degree type 1 heart block usually does not progress to a worse (third degree) form of heart block. If this does happen, then the heart rate would likely be very low and the patient would have a high probability of needing a pacemaker.
Some medications can cause heart block (or make it worse). Beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, or any other medications that inhibt the AV node should be reduced in dose or discontinued if this is safe to do.
Causes of Second degree Type 1 heart block:- ischemia (the AV node branch of the right coronary artery supplies the AV node)
- high vagal tone in athletes
- heart surgery
- medications that suppress the AV node (beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, other anti-arrhythmics)
Examples: